Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as HF&E), also known as comfort design, functional design, and systems, is the practice of designing products, systems, or processes to take proper account of the interaction between them and the people who use them. Proper ergonomic design is necessary to prevent repetitive strain injuries and other musculoskeletal disorders, which can develop over time and can lead to long-term disability.
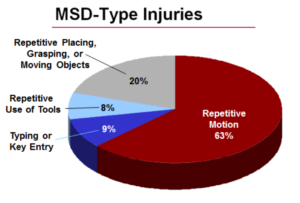
In June of 2016, ISPI completed an ergonomic risk assessment at a 104,000 SF roofing manufacturing facility in Corona, CA. The assessment was based on several different elements including: observations of various manufacturing stations selected by the client; informal interviews with manufacturing workers and supervisors; review of worker incident/complaint history in these areas; and discussions with site EHS. Each of the operations selected for ergonomic review were assessed using both quantitative and qualitative techniques (see below). Potential problem areas with increased risk were identified and recommendations were included to assist with reducing the risk of injury to workers. You may obtain further information regarding Ergonomics at California Occupational Safety and Health Administration (CAL/OSHA), California Code of Regulations (CCR) Title 8, §5110.
Qualitative: Detailed description of situations, events, people, interactions, and observed behaviors, the use of direct quotations from people about their experiences, attitudes, beliefs, and thoughts.
Quantitative: Distinguished by emphasis on numbers, measurement, experimental design, and statistical analysis. Large numbers of cases may be analyzed using quantitative design, and this type of design is deductive in nature, often stemming from a preconceived hypothesis.
